Would you believe it if we said there’s another technology that boasts just as many use cases as blockchain?
Indeed, blockchains aren’t the only decentralized systems as commonly perceived.
Technologies like Direct Acyclic Graph (DAG) are breathing new life into the cryptocurrency world.
While sharing plenty of similarities with blockchain, DAG tech is rising as the next step in the evolution of decentralized systems.
So, let’s find out in this article what they are, their design to fit the real-world use cases, and how they contrast with blockchain.
Let’s go!
Overview of DAG
DAG technology, or directed acyclic graph, is an approach to organizing and handling data, particularly in cryptocurrencies. It is like a system of connected dots rather than blocks in a blockchain. Instead of blocks, you have vertices and edges.
Transactions in DAG are represented as these vertices, and they’re stacked upon one another. Just like in a blockchain, nodes add transactions, but here, nodes need to perform proof-of-work tasks to submit a transaction.
The big difference? While blockchains resemble a linear chain, DAG looks more like a network of points. DAG is gaining greater interest because it might solve some issues in blockchain systems. With DAG, miners won’t be competing to add new blocks, and because nodes can be created simultaneously, transactions can be processed faster.
Now, how does it actually work?
- The DAG Setup: Imagine a web, not a chain, handling transactions in a new system called DAG. It’s like a tree with nodes (transaction points) connected all around. What’s more interesting here is these nodes can link to multiple others, allowing lots of transactions to happen at the same time.
- Referencing the Past: So, for a new transaction to be legit, it must point back to older ones, much like blocks in a blockchain refer to previous ones. The idea is that a transaction is only validated when it’s referenced by another, creating a chain of confirmations.
- No Blocks: Each transaction is a vertex in a DAG, and there are no blocks. No mining is needed, either. Transactions just build on top of each other, and proof-of-work tasks happen when a node submits a transaction to validate the ones before it and prevent spam.
- More Connections, More Options: Unlike blockchains that stick to one previous block, DAG-based transactions can point to multiple past ones. Some systems even use algorithms to choose which transactions to build on based on their weight or the number of confirmations received.
- Verifying Path to the Start: To avoid double spending, nodes confirm older transactions by following a path back to the first transaction in the DAG. This verifies if the sender has enough balance. If someone tries to build on an invalid path, their transaction might get ignored.
- Resolving Conflicts: When paths collide, an algorithm steps in, favouring transactions with a more solid history. This algorithm ensures the system stays on track.
The Dominating Advantages of DAG Technology
Lightning-fast Transactions
One of the most note-worthy attributes of DAG tech is its rapid transaction speed. Its structure allows for concurrent transaction approval, enabling users to initiate and receive confirmations simultaneously.
Handling Loads of Transactions
DAGs boast a superior throughput, processing a remarkable number of transactions per second (tps). Unlike traditional blockchains constrained by block generation times, DAGs effortlessly scale as more participants join.
Unparalleled Performance
Unlike traditional blockchains that experience congestion and performance degradation during spikes in transaction volume, DAG networks thrive under increased traffic. As the transaction load surges and user engagement intensifies, DAG systems exhibit improved performance.
Cost-Effective
The omission of the miner validation significantly reduces transaction fees within DAG networks. This streamlined process enables more transactions to be accommodated without the fear of escalating fees.
Energy-conscious
DAG protocols avoid the energy-intensive PoW consensus mechanism, setting them apart as eco-friendly alternatives to PoW-based blockchains. As cryptocurrencies like BTC face scrutiny regarding their impact, DAGs offer a solution by significantly reducing energy consumption.
Versatile Implementation
DAGs exhibit versatility beyond currency applications. Their compatibility with diverse consensus mechanisms allows seamless integration into various sectors such as IoT, supply chains, and other specialized domains.
Altogether, their scalability and resilience make DAG ideal for platforms anticipating high transaction volumes.
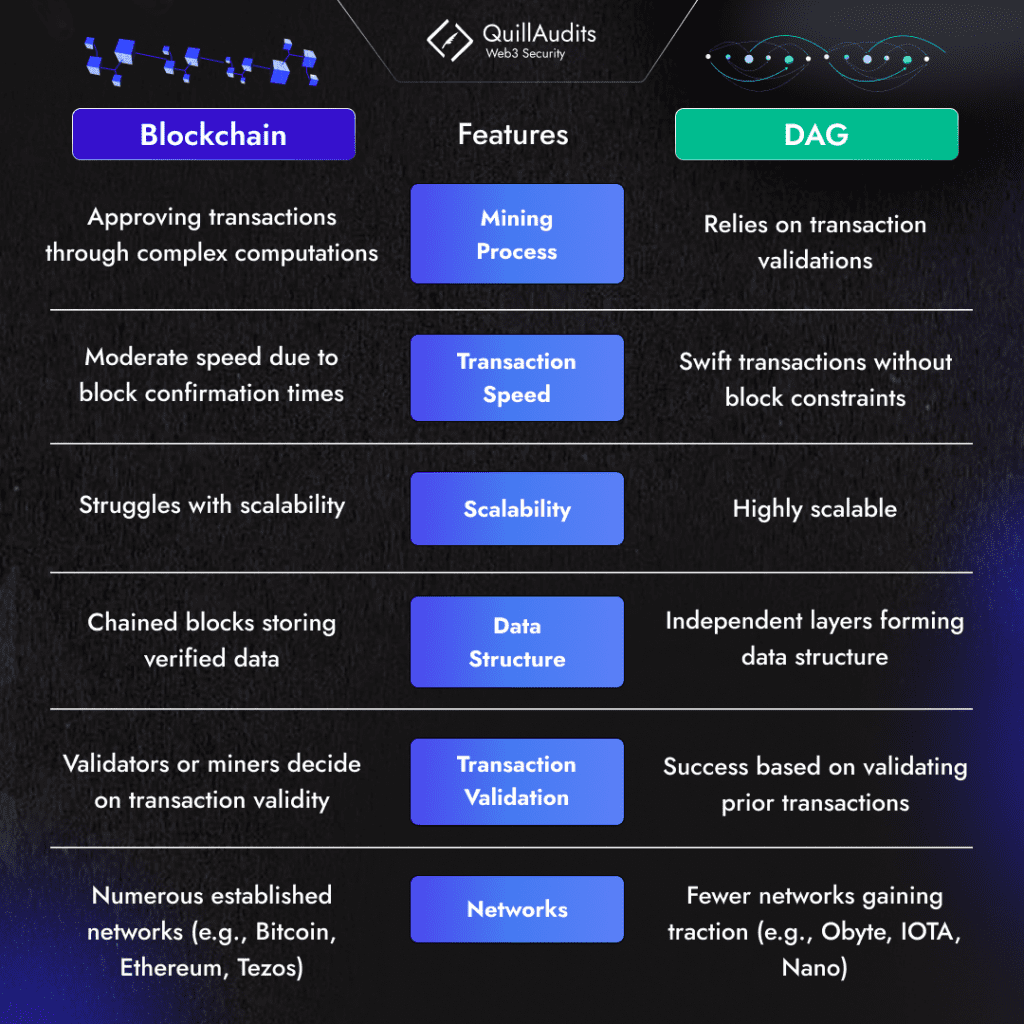
DAG vs. Blockchain – Analysing Their Technical Distinction
- Mining: Approving Transactions vs. Transaction Validation
In blockchain, mining involves approving transactions and creating new coins through complex computations. Miners confirm and add transactions to blocks, earning tokens in return.
In contrast, DAG’s consensus relies on previous transaction validations. Transactions gain consensus by referencing prior ones with substantial weight.
- Transaction Speed: Absence of Blocks vs. Scalability
Blockchains are known for speed, but DAGs take the lead. Without block or wait times, DAGs ensure swifter transactions.
While blockchain struggles with scalability, DAG’s unique structure allows for a high volume of transactions, enhancing scalability.
- Data Structure: Chained Blocks vs. Independent Layers
Verified data resides within linked blocks in blockchains, forming an endless chain. In DAG, data is stored independently, creating layers on top of each other.
- Transaction Validation: Miner Decision vs. Approval of Previous Transactions
Blockchains rely on miners or validators to decide on transaction validity. In DAG, a transaction’s success hinges on its ability to validate prior transactions.
- Networks: Wide Blockchain Adoption vs. Limited DAG Networks
Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Tezos are among the many blockchain networks. In contrast, DAG networks like Obyte, IOTA, and Nano are fewer but gaining traction.


DAG-powered Projects
TARAXA
- TARAXA incorporates BlockDAG technology to enhance scalability while maintaining robust security measures.
- This implementation allows for high throughput, surpassing 5,000 TPS.
- It has outlined a roadmap with ambitious plans to elevate its performance further, aiming for an impressive 50,000 TPS.
IOTA
- IOTA stands out with its utilization of Tangle, a DAG-based structure aimed at overcoming the limitations of traditional blockchain architectures.
- Tangle’s design facilitates near-instant, fee-less transactions, ideal for IoT applications.
- Its multidimensional structure fosters interconnected transactions, eliminating the need for separate blocks or chains and enhancing scalability and performance.
- The platform’s testnet has demonstrated impressive scalability, achieving over 10,000 TPS.
Nano
- Nano adopts the innovative block-lattice framework, a hybrid combining DAG principles with traditional blockchain. This structure allows for independent blockchains for each user within the network.
- Nano’s architecture enables simultaneous transactions of any size without incurring network fees.
- Each user manages their own blockchain, providing a high degree of autonomy and security. Nano prioritizes high-speed transactions and zero transaction fees.
Final Thoughts
Considering the landscape we’ve explored, both blockchain and DAG showcase strengths and differences. It’s not about one being definitively better than the other, but rather about their fit for specific tasks. Each has its own pros and cons, tailored for different needs.
Embracing their unique strengths allows for creating more efficient and adaptable systems, elevating innovation in the crypto space.
Curious about leveraging Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)? Chat with our QuillAudits experts to turn your vision into a secure decentralized reality.