Introduction
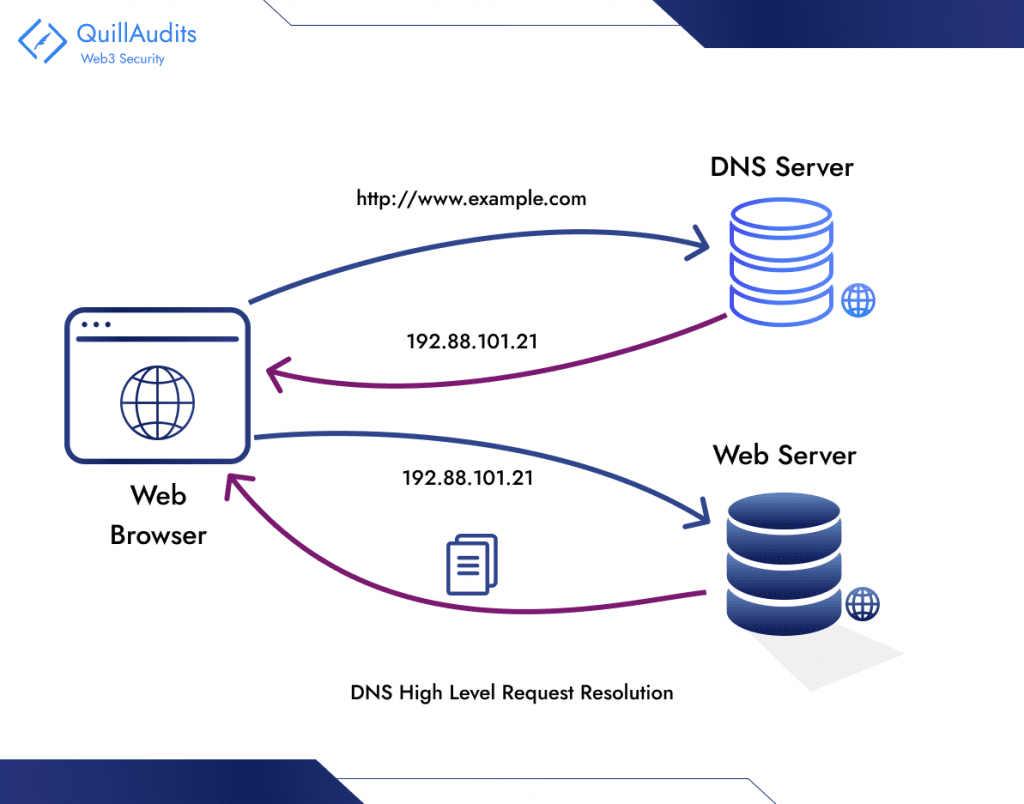


DNS security is vital for a safe online space. DNS translates domain names to IP addresses, crucial for internet functionality. DNS ensures unique name-value pairs and maintains a consistent database view for all participants. However, vulnerabilities in this system can have significant consequences:
- Disrupted access: DNS attacks redirect users, blocking access to legitimate sites, and may expose them to phishing or malware threats.
- Data breaches: Hacked DNS records enable theft of sensitive data by directing users to fraudulent websites.
- Business disruption: DNS attacks causing downtime can result in major financial losses and harm an organization’s reputation.
These consequences go beyond immediate impacts. DNS attacks often have cascading effects:
Compromised trust: A successful attack on a trusted organization can erode user confidence in online interactions, impacting other businesses and services.
Expanded attack surface:DNS vulnerabilities can grant attackers network access, facilitating additional internal system and data breaches.
Internet interconnectivity means cybersecurity threats aren’t isolated; weakness in one area can create vulnerabilities elsewhere. Holistic security is vital, safeguarding DNS, network infrastructure, user devices, and applications comprehensively. Organizations can bolster defenses and limit attack consequences with a holistic security approach.
This section emphasizes DNS security’s importance and consequences. We’ll explore real-world examples and mitigation strategies to understand cascading effects.
What is DNS Hijacking?
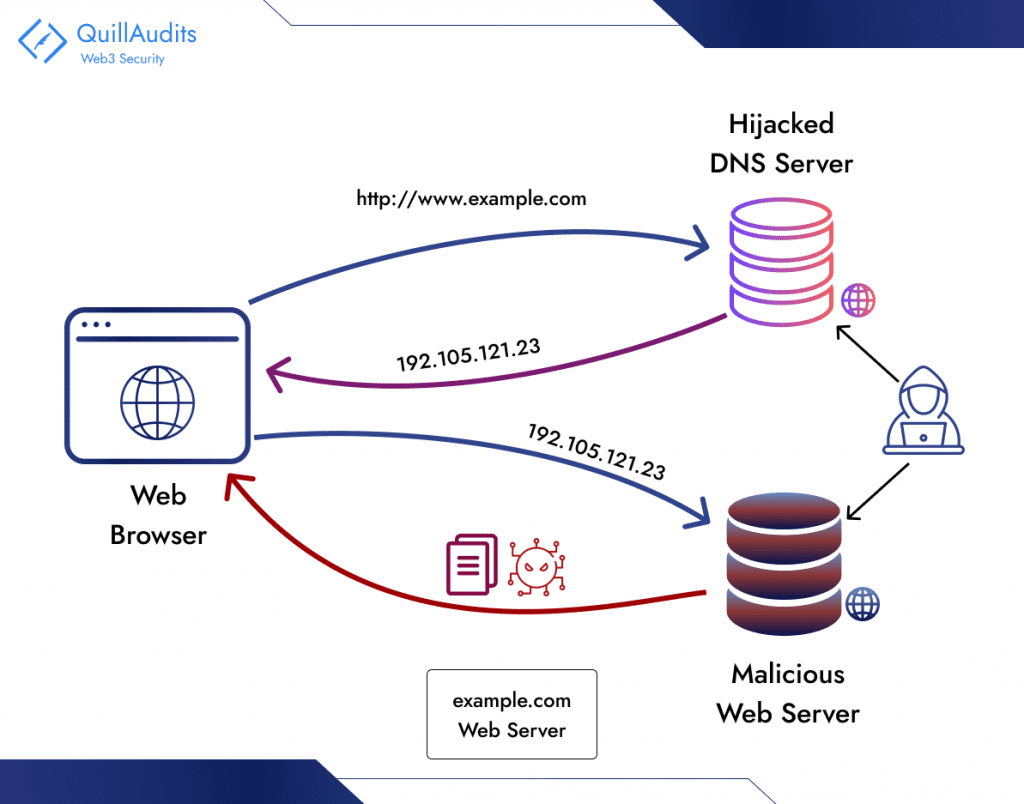


DNS hijacking disrupts the Internet by corrupting DNS records, potentially blocking access or redirecting users to malicious sites. Attackers often replace legitimate domain IP addresses with malicious ones by manipulating DNS for cyber attacks. This change redirects DNS queries to malicious servers, deceiving users into accessing fake websites unknowingly. Users unknowingly visit compromised sites via tampered servers, risking phishing and malware threats compromising their devices.
Common Cascading Effects of DNS Attacks
Phishing Attack
Phishing attacks aim to steal your personal information, like passwords or credit card details, by tricking you into entering them on a fake website. Hackers exploit compromised DNS entries, manipulating how computers translate website names into addresses for malicious purposes. Here’s how it works:
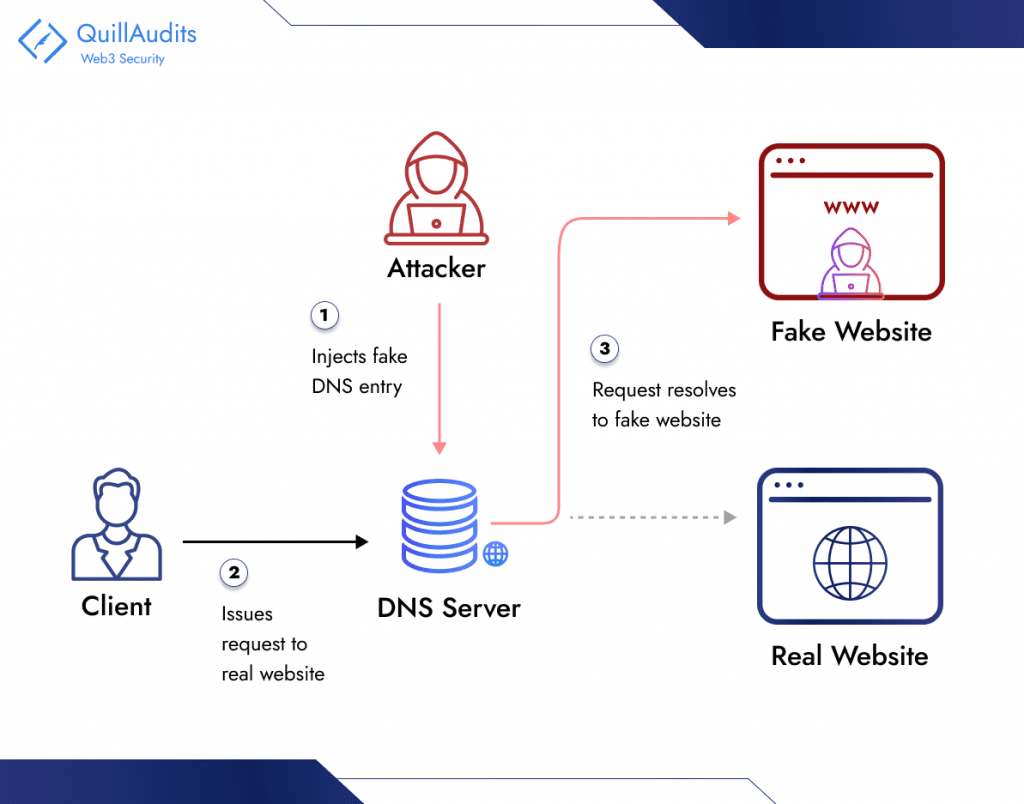


1. Compromising the DNS:
Attackers can target:
- DNS servers: These servers act like phonebooks for the internet, translating domain names (e.g., “[invalid URL removed]”) into IP addresses (e.g., “172.217.160.66”). By compromising a server, attackers can alter the information it provides.
- Individual devices: Malware or compromised routers can manipulate the DNS settings on your computer, forcing it to use specific DNS servers controlled by the attacker.
2. Redirecting to the Phishing Site:
Once attackers have control over the DNS resolution process, they can:
- Change the IP address linked to a legitimate domain: A compromised DNS server redirects real website addresses to similar-looking malicious sites.
- Create fake DNS entries: Attackers can create entries for non-existent domains that closely resemble real ones. When you enter such a domain, you’ll be taken to the attacker’s phishing site.
3. The Phishing Trap:
Attackers replicate authentic websites, tricking users into sharing sensitive data, assuming they’re on genuine sites. This information is then captured by the attacker and used for malicious purposes like identity theft, financial fraud, or further attacks.
Malware Distribution
DNS hijacking is a cyberattack where attackers manipulate the Domain Name System (DNS) to redirect users from legitimate websites to malicious ones. It’s used for malware distribution through poisoned caches and malicious redirects.
1. Poisoned Caches:
- Mechanism: Exploiting DNS server vulnerabilities to inject false information, leading users to malicious servers.
- Malware Distribution: Users are directed to malicious servers instead of legitimate websites, potentially exposing them to malware.
2. Malicious Redirects:
- Mechanism: Modifying DNS settings to redirect users to malicious websites.
- Malware Distribution: Malicious websites can distribute malware through drive-by downloads, phishing attacks, and social engineering tactics.
Data Breaches
Compromised DNS servers enable data theft through man-in-the-middle attacks and data exfiltration:
Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
DNS Hijacking: Redirecting users to fake sites to steal login details and personal info.
Intercepted Communication: Stolen data leads to account takeover and identity theft.
Data Exfiltration
DNS Tunneling: Attackers can exploit the DNS protocol to exfiltrate sensitive data from compromised systems. They encode the data and send it in small chunks within DNS requests, making it appear like legitimate DNS traffic. This technique can be used to steal:
Confidential documents: Attackers can exfiltrate sensitive documents, such as financial records, trade secrets, or intellectual property.
User credentials: Stolen login credentials can be exfiltrated through DNS tunneling and used for further attacks within the network.
Bypassing security measures: Traditional security tools might not be able to detect data exfiltration through DNS due to its disguised nature, allowing attackers to steal information undetected.
Ransomware attacks:
Ransomware attacks using DNS disruptions are especially dangerous as they block critical systems without file encryption. Here’s a breakdown:
1. Initial Compromise: Attackers gain network access via phishing, exploiting vulnerabilities, or stolen credentials.
2. Lateral Movement: They move within the network to target DNS servers or management interfaces.
3. DNS Disruption: Attackers seize DNS control, altering records to divert traffic from legitimate services.
4. Exploitation and Extortion: Victims discover the attack when services are inaccessible, receiving ransom demands for DNS restoration.
5. Impact: Disrupted services, data theft threats, and persistent access risks affect operations and reputation.
6. Mitigation and Response: Incident response, DNS configuration monitoring, and backups are crucial.
7. Prevention: Security training, vulnerability management, and network segmentation are key.
Understanding these tactics is vital for robust security strategies, especially for QuillAudits, to safeguard digital assets against such ransomware attacks.
Real-World Example of DNS Attack
Curve Finance
On August 9th, 2022, Curve Finance reported a DNS hijack affecting its website interface.
The attacker replaced the project’s frontend with a malicious one, leading users to unwittingly approve unauthorized transfers. Users, interacting with the altered frontend, wrongly assumed they were approving transfers via official contracts. In reality, users unknowingly granted approval for their funds to be directed to the attacker’s contract address. When approved, this drained users’ wallets, resulting in a $570k loss for Curve Finance. Again, credentials to access the project’s DNS record, managed by Iwantmyname, were stolen. This enabled the attacker to substitute the legitimate IP address mapping with malicious ones. The webpage’s code was altered to swap the legitimate address for swapping operations with a malicious one.
The hack did the attack via below steps:
Step 1 – DNS hijack redirect users to a malicious URL. Users unknowingly authorized transactions to the hacker’s contract, leading to loss.
Step 2 – The hacker’s contract, with user token authorization, can transfer tokens from the user’s wallet to the hacker’s specified address.
Step 3 – Hackers traded the tokens gained from the attacks on decentralized exchanges and then laundered them using Tornado.Cash.
Mitigating Related Hacks
Cybersecurity threats are ever-evolving, but staying proactive doesn’t have to be overwhelming. Here are key strategies to mitigate related hacks:
Email Security: Deploy DMARC, SPF, and DKIM like shields to deflect email spoofing and phishing attempts. These protocols verify email sender legitimacy, minimizing the risk of falling victim to fraudulent messages.
Website Stronghold: Fortify your website with HTTPS encryption and secure coding practices. This duo acts as a moat and gatekeeper, preventing vulnerabilities and malware infiltration.
Multi-Factor Authentication: Add an extra layer of security to user accounts with MFA. This “double-door” approach requires not just a password, but an additional verification step, significantly reducing unauthorized access risk.
Endpoint Protection: Equip devices with antivirus and endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions. They work like diligent guards, watching out for and stopping malware and unauthorized access attempts.
Educate & Empower: Regular security awareness training equips employees to identify threats and practice safe online behavior. This human firewall is crucial in the fight against cyberattacks.
Monitor & Analyze: Keep a watchful eye on your DNS activity with monitoring and logging. This vigilance helps detect suspicious behaviour and potential threats before they escalate. For this you can use DNS Monitor by Dappling Network to track changes in Web3 domain nameserver settings.
Firewall Shield: Deploy a DNS firewall to act as a proactive barrier against malicious traffic. This additional layer blocks known attack vectors, further safeguarding your systems. Implementing these strategies enhances defence, fostering a safer digital environment.
Conclusion
DNS attacks pose significant threats to internet stability and security, with far-reaching consequences for users and organizations. From phishing to ransomware, these attacks have consistent harmful potential. Understanding the threats is key to effective mitigation. Strategies like email security, encryption, and employee education are crucial. By adopting layered defenses, organizations can reduce vulnerability. Vigilance is essential for all stakeholders, and resources are available for further learning. Let’s prioritize cybersecurity for a safer digital future.
Explore these resources for a deeper understanding of DNS attacks and real world examples :-
Galxe, a Web3 platform, suffers DNS attack on front-end site
FAQs
1. What are some technical mitigation strategies against DNS attacks in the Web3 and blockchain ecosystem?
DNSSEC enhances security by authenticating DNS responses, reducing DNS spoofing risks. Encourage Web3 wallet usage with extra security features. Explore decentralized DNS options for resilience. Implement Content Security Policies on Web3 interfaces to prevent malicious script loading. Regular audits and DNS traffic monitoring help identify and mitigate threats promptly.
2. How does DNS cache poisoning affect Web3 and blockchain services?
DNS cache poisoning involves inserting false information into the DNS cache, leading users to malicious sites instead of the intended Web3 or blockchain service. Users interacting with fake interfaces risk losing digital assets or sensitive data, assuming they’re genuine.
3. What are the best practices for Web3 developers to prevent DNS-related vulnerabilities in their applications?
Adopt decentralized web tech like IPFS to reduce reliance on traditional hosting. Use domain whitelisting and conduct regular security audits.