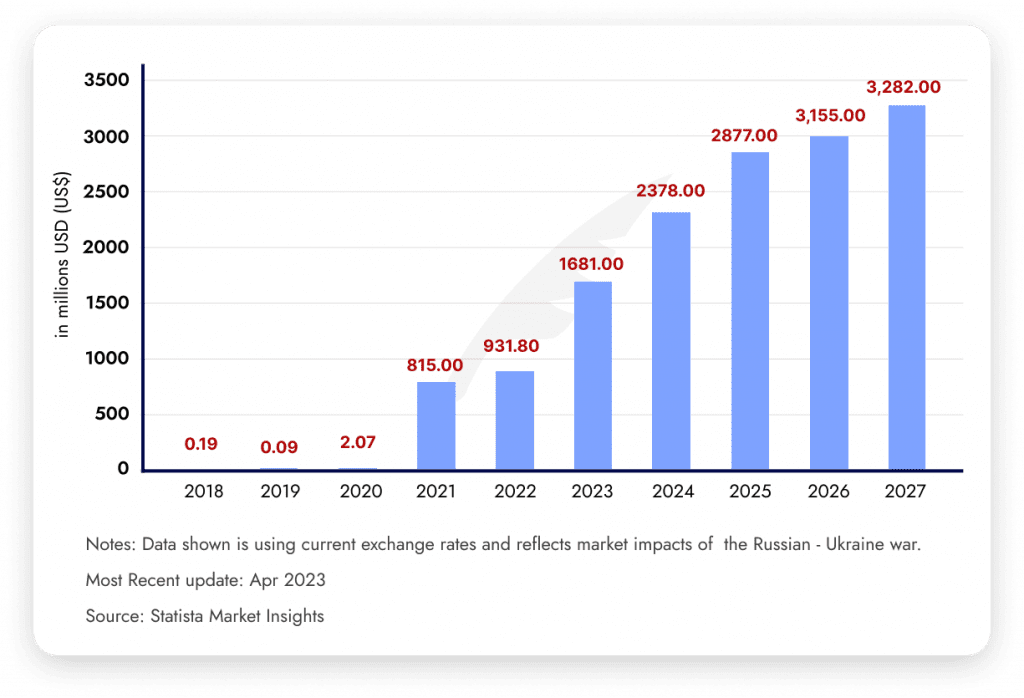
According to statista.com projections, the non-fungible token (NFT) market is expected to experience significant growth in terms of both revenue and user engagement.
The NFT market is anticipated to generate roughly US$2,378.00 million in revenue by 2024. With a predicted annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.34% between 2024 and 2027, this rising trend is expected to continue, resulting in a projected total revenue of US$3,282.00 million by 2027.
The US is projected to dominate the NFT market in 2024, with average revenue per user reaching US$140 and total sales hitting over US$1 billion. Despite its explosive growth, NFT participation remains niche, with only 0.2% of the global population expected to be involved by 2027. However, the burgeoning rise of the NFT market does not come without its challenges.


However, the whopping rise doesn’t mean NFTs are free of issues. NFTs are built on smart contracts that are prone to exploitation and hacking. According to Bitcoin News, 25% of all smart contracts have critical bugs. Apart from these, other contracts are also likely to contain bugs of various types and severity levels. Developers, often working in a hurry or because of a lack of knowledge, may create faulty contracts, which might cause the loss of millions of dollars to the project promoters.
Security problems in NFTs can also result from smart contract vulnerabilities. They consist of front-running, reentry, and DoS attacks. Furthermore, the industry’s inadequate identity verification practices have led to the sale of counterfeit artwork.
NFT Security Issues And Dangers
- Marketplace Risks:- By using a marketplace to purchase and store digital art, you are giving third parties access to your NFT security. Security flaws in NFT Marketplaces are exploited by bad actors to steal money or obtain unauthorized access to your assets. Examples include the Lympo hot wallet security breach, the Full Send Metacarrd, and the OpenSea low-price exploit.
- Rugpulls:- A rug pull in the NFT world is a scam where the creators of an NFT project hype it up, sell NFTs for cryptocurrency, and then suddenly withdraw all the funds and disappear, leaving investors with worthless NFTs.
An example is the “Evolved Apes” case, where the creator vanished with about $2.7 million, and the promised features of the project were never delivered. This illustrates the risks in the speculative and largely unregulated NFT market. 2022 was full of scamming projects, such as AniMoon, Frosties, Boren Bunnty, and Big Daddy Ape Club. These scams have led to millions in stolen value. In most cases, founders run off with users’ assets. While rug pulls are not technically hacks, they result in unintended losses. Thus, you better learn how to avoid them. - Smart Contract Vulnerability:- NFTs on Ethereum use a set of rules called ERC-721, along with ERC-998 and ERC-875, with similar standards like BEP-721 on BNB Smart Chain and TRC-721 on Tron. These digital contracts have a risk of flaws since they are public, allowing hackers to find and exploit weaknesses to steal tokens.
These vulnerabilities often stem from coding errors in languages like Solidity, Vyper, or Rust, and since these contracts run in a simulated environment like the Ethereum Virtual Machine, any coding mistake can disrupt the entire contract. Additionally, since these contracts frequently interact with each other, a single error can cause not just one application to fail, but also affect other interconnected services.
Most Common Smart Contract Issues
- Reentrancy
- Arithmetic Overflows and Underflows
- Default Visibilities
- Race Conditions
- Denial of Service (DOS)
- Constructors with Care
Let us throw light on some popular NFT projects that experienced fatal outcomes due to bugs and mischievous tweaks:
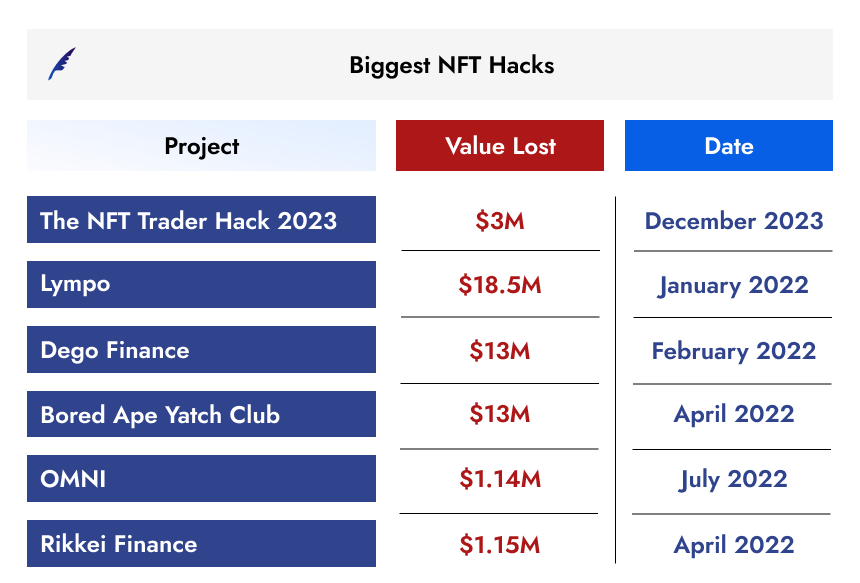


The NFT Trader Hack 2023
NFT Trader fell victim to a hack in December 2023. The attacker took advantage of weaknesses in the smart contracts of the project to steal valuable NFTs valued at approximately $3 million.
The reentrancy vulnerabilities present in a number of the project’s older smart contracts provided the NFT Trader attackers with an opening. A security hole in a smart contract’s internal state tracking when it calls other, untrusted smart contracts is known as a reentrancy vulnerability.
When a withdrawal function is implemented, for instance, the smart contract might verify that a withdrawal request is legitimate, give the caller access to the assets, and then update its records to show that the withdrawal was completed successfully.
This control flow is problematic because a smart contract can execute its own code upon receiving a transfer. This feature allows a malicious smart contract to re-enter the susceptible withdrawal function before it has had a chance to update its internal state. The attacker would be able to take out the same assets more than once thanks to this.
OMNI Real-Estate Token Exploit
In January 2023, the Omni Real Estate token on the BNB Smart Chain was compromised due to coding flaws in its smart contract. The issues involved integer overflow/underflow, where numbers exceed or drop below the storage limit, leading to incorrect values.
Additionally, there was improper argument validation, meaning the contract failed to adequately check the inputs it received. These vulnerabilities allowed unauthorized actions within the smart contract, underscoring the need for rigorous security measures in cryptocurrency development.
OpenSea Low-Price Exploit (January 2022)
OpenSea, a major online marketplace for NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens), faced a serious security issue when hackers found a way to steal valuable NFTs, including popular ones like Bored Apes, at very low prices. The theft was cleverly done using a flaw in OpenSea’s system that handled listing cancellations. Hackers exploited a back-end vulnerability and purchased NFTs at lower prices.
They resold them for more than 300 ETH, over $700K. The old listing was still accessible through OpenSea API. The breach highlighted a big security problem in the rapidly growing NFT market, showing the risks of using new and unproven digital contracts. OpenSea quickly fixed the issue, but the damage to its reputation was already done.
The Significance of Smart Contract Examination in an NFT Project
Any blockchain project must perform a smart contract audit in order to find and fix any code vulnerabilities that might result in asset loss or reputational harm. An audit of this kind examines the codebase for a wide range of possible problems, such as reentrancy attacks, gas limit problems, and logical and numerical errors. It also evaluates the security of random number generation and protects against vulnerabilities that could cause a denial of service.
After conducting a thorough vulnerability analysis, auditors rank security vulnerabilities according to their level of severity. This results in a comprehensive report that not only identifies issues that need to be fixed right away but also makes recommendations for improvements that will increase the smart contract’s efficiency and security.
QuillAudits stands at the forefront of smart contract security, offering an NFT Due Diligence Service that is unmatched in its thoroughness and reliability. Harness the power of our expertise to preempt the plethora of NFT attack vectors, including smart contract vulnerabilities, marketplace bugs, and the increasingly sophisticated threats posed by social engineering tactics.
How can users lower their risk exposure?
- Use trustworthy NFT marketplaces only, and keep your coins safe in a secure wallet.
- Be on the lookout for NFT scams and confirm the legitimacy of any offers before sending money or NFTs.
- When it is feasible, use multi-factor authentication.
- Prior to signing any transaction using NFTs through their wallets, review the transaction details.
Conclusion
In summary, despite the rapid growth of the NFT market, security vulnerabilities persist. The NFT market is projected to reach a revenue of US$3,282.00 million by 2027. Notable security breaches like the NFT Trader Hack of 2023 and the OpenSea Low-Price Exploit serve as evidence of these vulnerabilities. These breaches often stem from smart contract flaws, leading to substantial financial losses. Common smart contract vulnerabilities include reentrancy, arithmetic overflows, and denial of service attacks.
Individual users can mitigate risk in the NFT space by utilizing trustworthy marketplaces, safeguarding their funds in secure wallets, staying vigilant against scams, and diligently verifying transaction details before confirming. To ensure the NFT market’s growth and security, proactive security measures, such as smart contract audits, are vital. Developers and investors must stay informed about evolving security threats as the market evolves.